Traefik as API Gateway
Tue 12 March 2019
API gateway acts as a reverse proxy, routing API requests from clients to services. Usually it also performs authentication and rate limiting, so the services behind the gate don't have to. In this short tutorial we'll see how to achieve that with Traefik reverse-proxy.
The demo is based on a dummy Traveling project where we have services to rent a car and book a hotel.
Firstly, we shall install Traefik on Minikube as an Ingress Controller by following Traefik user guide. Ingress Controller is a Pod that's responsible for fulfilling the Ingress: it watches the /ingresses Kubernetes endpoint for updates to satisfy requests for Ingresses. Ingress exposes HTTP routes from outside the cluster to Services within the cluster. HTTP traffic routing is controlled by rules defined on the Ingress resource.
$ minikube start
Starting local Kubernetes v1.13.2 cluster...
$ kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/containous/traefik/master/examples/k8s/traefik-rbac.yaml
$ kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/containous/traefik/master/examples/k8s/traefik-deployment.yaml
Traefik ingress service (port 80, NodePort 32518) is the entry point of our API gateway.
$ minikube service list
|-------------|-------------------------|--------------------------------|
| NAMESPACE | NAME | URL |
|-------------|-------------------------|--------------------------------|
| default | kubernetes | No node port |
| kube-system | kube-dns | No node port |
| kube-system | traefik-ingress-service | http://192.168.99.100:32518 |
| | | http://192.168.99.100:31735 |
|-------------|-------------------------|--------------------------------|
$ TRAEFIKURL=http://192.168.99.100:32518
$ curl $TRAEFIKURL
404 page not found
Note, there is also Traefik admin dashboard (port 8080) running at http://192.168.99.100:31735.
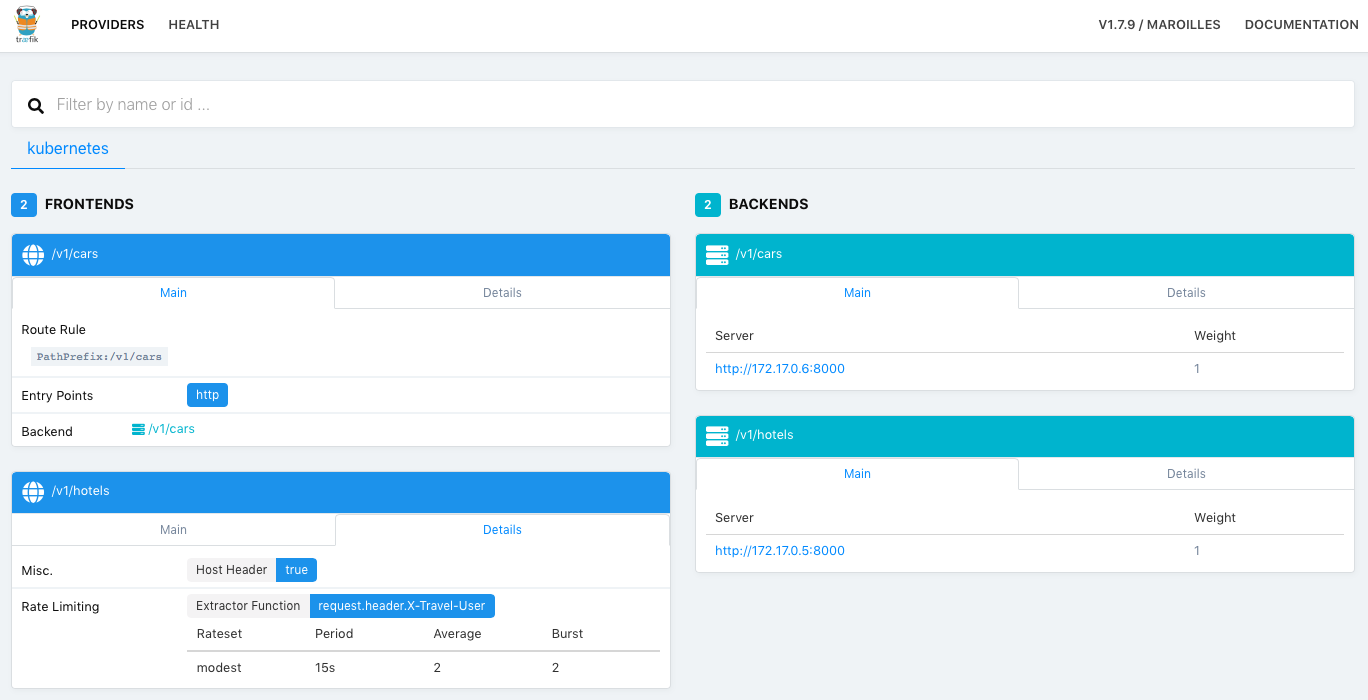
Travel Apps
Let's deploy the travel apps on Kubernetes. For simplicity, you can use the images uploaded to Docker Hub. If you prefer to build Docker images yourself, make sure they are accessible from Minikube: configure Docker client to communicate with the Minikube Docker daemon. Note, you can restore your local Docker environment with eval $(minikube docker-env --unset) later on.
$ git clone https://github.com/marselester/apigate.git
$ cd ./apigate/
$ eval $(minikube docker-env)
$ docker build --tag=marselester/travel-hotel:v1.0.0 --file=docker/hotel.Dockerfile .
$ kubectl apply -f k8s-traefik/hotel/deployment.yml
$ kubectl apply -f k8s-traefik/hotel/service.yml
The hotel app should be running:
$ kubectl get pods -l app=hotel
hotel-api-8d7d59b69-bcsvh
$ kubectl port-forward hotel-api-8d7d59b69-bcsvh 8000
$ curl localhost:8000/v1/hotels/bookings/7b4fc183-ee67-494d-9715-3510c6d8f2ef
{
"id": "7b4fc183-ee67-494d-9715-3510c6d8f2ef",
"hotel_id": "046d471d-70c7-4595-80cc-266d3e6e07fa",
"status": "confirmed"
}
Now, it's time to put the hotel Service behind the gateway by creating an Ingress rule.
$ kubectl apply -f - <<<'
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: hotel-ingress
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /v1/hotels
backend:
serviceName: hotel
servicePort: 80
'
Hotel booking requests should be routed to the hotel app:
$ curl $TRAEFIKURL/v1/hotels/bookings/7b4fc183-ee67-494d-9715-3510c6d8f2ef
{
"id": "7b4fc183-ee67-494d-9715-3510c6d8f2ef",
"hotel_id": "046d471d-70c7-4595-80cc-266d3e6e07fa",
"status": "confirmed"
}
The car rental app is deployed similarly.
$ docker build --tag=marselester/travel-car:v1.0.0 --file=docker/car.Dockerfile .
$ kubectl apply -f k8s-traefik/car/deployment.yml
$ kubectl apply -f k8s-traefik/car/service.yml
$ kubectl apply -f - <<<'
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: car-ingress
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /v1/cars
backend:
serviceName: car
servicePort: 80
'
You can see that the car booking is available at the gateway.
$ curl $TRAEFIKURL/v1/cars/bookings/9e0d65f5-9de2-4428-9bee-1f3967f05129
{
"id": "9e0d65f5-9de2-4428-9bee-1f3967f05129",
"car_id": "cfb6f7a5-4591-4f5c-8b17-9a1b10f98ada",
"status": "confirmed"
}
Authentication Service
API requests must be authenticated before reaching the Travel apps. This work is delegated to travelauth Service that performs HTTP Basic authentication and returns a username in X-Travel-User header if credentials matched. We shall start from deploying it on the cluster.
$ docker build --tag=marselester/travel-auth:v1.0.0 --file=docker/auth.Dockerfile .
$ kubectl apply -f k8s-traefik/auth/deployment.yml
$ kubectl apply -f k8s-traefik/auth/service.yml
If the auth server is properly deployed, it will prompt for username/password.
$ kubectl get pods -l app=auth
auth-api-556685f658-h9qb4
$ kubectl port-forward auth-api-556685f658-h9qb4 8000
$ curl -i -u bob:bob localhost:8000/v1/hotels
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
X-Travel-User: bob
Let's tell Traefik to forward all requests to the auth server and copy X-Travel-User response header from the auth server to the routed request.
[entryPoints]
[entryPoints.http]
address = ":80"
[entryPoints.http.auth.forward]
address = "http://travelauth.default/"
authResponseHeaders = ["X-Travel-User"]
Create a ConfigMap entry for the Traefik config file and mount traefik-conf ConfigMap volume to traefik-ingress-controller Pod.
$ kubectl create configmap traefik-conf --from-file=traefik.toml=k8s-traefik/traefik/traefik.toml --namespace=kube-system
$ kubectl apply -f k8s-traefik/traefik/deployment.yml
The updated Traefik deployment is now enforces authentication on API gateway.
$ curl -i $TRAEFIKURL/v1/hotels/bookings/7b4fc183-ee67-494d-9715-3510c6d8f2ef
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
$ curl -i -u bob:bob $TRAEFIKURL/v1/hotels/bookings/7b4fc183-ee67-494d-9715-3510c6d8f2ef
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
{
"id": "7b4fc183-ee67-494d-9715-3510c6d8f2ef",
"hotel_id": "046d471d-70c7-4595-80cc-266d3e6e07fa",
"status": "confirmed"
}
Rate Limiting
Request rate limiting is configured via Ingress annotations. For example, we allow to send only 2 hotel requests per 15 seconds for each logged in customer.
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: hotel-ingress
annotations:
traefik.ingress.kubernetes.io/rate-limit: |
extractorfunc: "request.header.X-Travel-User"
rateset:
# Allow 2 requests every 15 seconds.
modest:
period: 15s
average: 2
burst: 2
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /v1/hotels
backend:
serviceName: hotel
servicePort: 80
Let's apply these limits onto the hotel app.
$ kubectl apply -f k8s-traefik/hotel/ingress.yml
$ for i in {1..3}; do curl -i -s -u bob:bob $TRAEFIKURL/v1/hotels/bookings/7b4fc183-ee67-494d-9715-3510c6d8f2ef | head -n 1; done
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
HTTP/1.1 429 Too Many Requests
As you can see the third request was throttled.
Although it's convenient enough to apply rate limiting using annotations, I would've preferred rate limiting to be decoupled from Traefik similar to authentication service.
Category: Infrastructure Tagged: traefik kubernetes api gateway auth rate limiting